How Do You Measure a Vibration Test?
What is a vibration test?
A vibration test is a type of test that is used to evaluate the response of a material or object to vibrational loads. These tests are often used to determine the fatigue life of a material or object, as well as its ability to resist damage from vibration. There are four main types of vibration tests: sine, random, shock, and transient. Sine testing is the most common type of vibration test and is used to identify resonance frequencies in the product. Random testing is used to simulate real-world conditions and to identify structural issues. Shock testing simulates sudden impacts or events, such as dropping a product. Transient testing simulates changes in velocity, such as when a product accelerates or decelerates during use.
How to measure a vibration test
There are many different ways to measure a vibration test, but one of the most common is to use an accelerometer. This device can be attached to the object that is being tested and will measure the acceleration of the object as it vibrates.
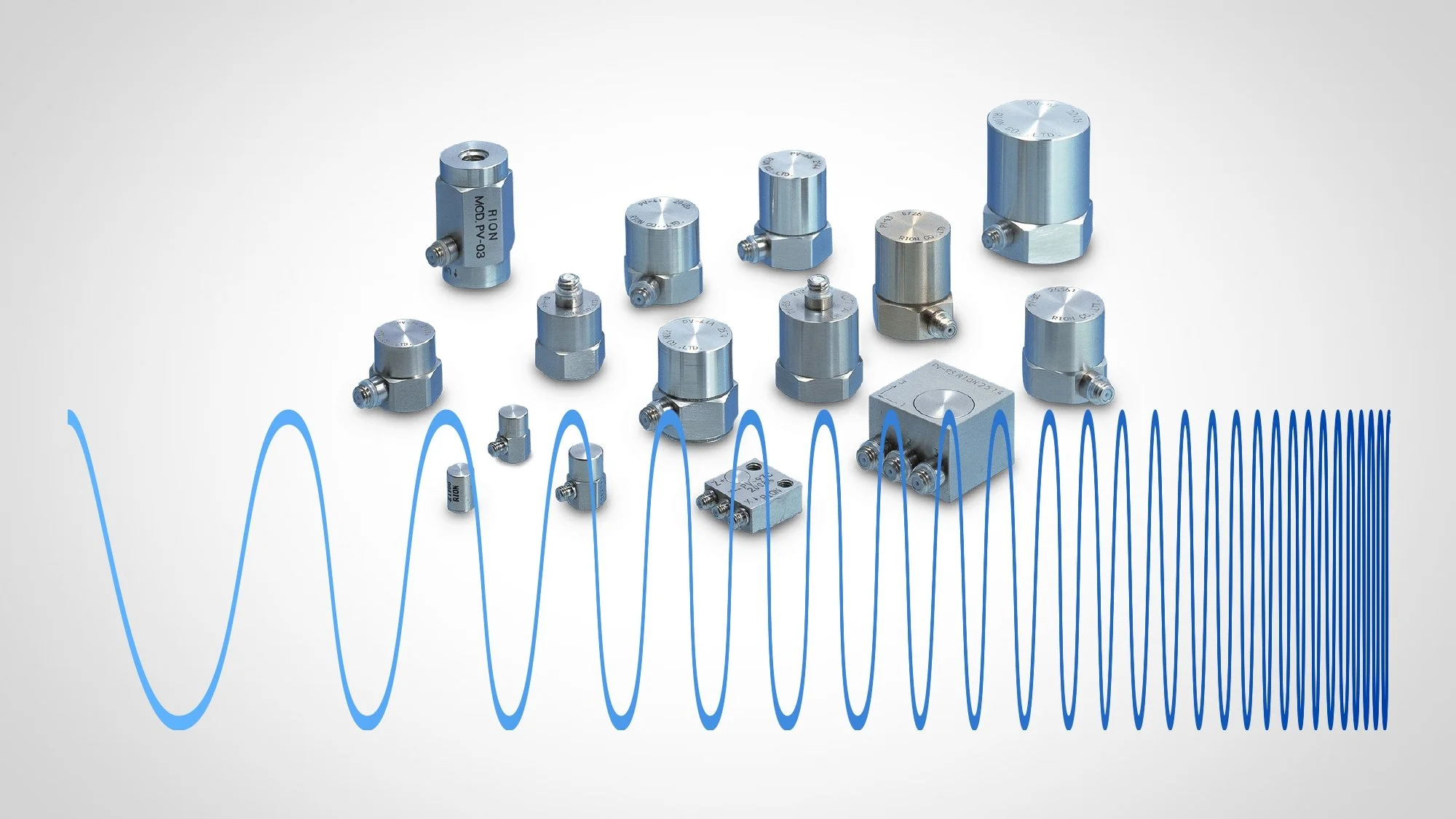
Vibration is most commonly measured using a ceramic piezoelectric sensor or accelerometer. An accelerometer is a sensor that measures the dynamic acceleration of a physical device as a voltage. Accelerometers are full-contact transducers typically mounted directly on high-frequency elements, such as rolling-element bearings, gearboxes, or spinning blades. These versatile sensors can also be used in shock measurements (explosions and failure tests) and slower, low-frequency vibration measurements. The benefits of an accelerometer include linearity over a wide frequency range and a large dynamic range.
Another sensor you can use to measure vibration is the proximity probe. Unlike accelerometers, which measure acceleration to determine vibration, proximity probes are non-contacting transducers that measure the distance to a target. These sensors are almost exclusively used in rotating machinery to measure the vibration of a shaft. An example of a common application is machine monitoring and protection measurements for mechanical systems like turbomachinery. Because of the flexible fluid film bearings and heavy housing, vibrations do not transmit well to the outer casing, so you use proximity probes instead of accelerometers to directly measure shaft motion.
Most accelerometers rely on the use of the piezoelectric effect, which occurs when a voltage is generated across certain types of crystals as they are stressed. The acceleration of the test structure is transmitted to a seismic mass inside the accelerometer that generates a proportional force on the piezoelectric crystal. This external stress on the crystal then generates a high-impedance, electrical charge proportional to the applied force and, thus, proportional to the acceleration.
Piezoelectric or charge mode accelerometers require an external amplifier or inline charge converter to amplify the generated charge, lower the output impedance for compatibility with measurement devices and minimize susceptibility to external noise sources and crosstalk. Other accelerometers have a charge-sensitive amplifier built inside them. This amplifier accepts a constant current source and varies its impedance with respect to a varying charge on the piezoelectric crystal. These sensors are referred to as Integrated Electronic Piezoelectric (IEPE) sensors. Measurement hardware made for these types of accelerometers provides built-in current excitation for the amplifier. You can then measure this change in impedance as a change in voltage across the inputs of the accelerometer.
Why is it important to measure vibration tests?
Vibration testing is an important process used to ensure the safety and quality of products. By measuring the vibration of a product, manufacturers can identify potential problems with the product and make necessary improvements. Additionally, vibration testing can help verify the strength and durability of a product before it is released to the market.
There are many reasons why it is important to measure vibration. Vibration can cause products to break or fail, and it can also be a sign of a problem with the manufacturing process. By measuring vibration, manufacturers can improve the quality of their products and prevent expensive failures. Additionally, vibration testing can help identify potential safety hazards.
Vibration testing is a key part of quality control for many products. It helps ensure that products can withstand the rigors of shipping and handling, as well as everyday use. There are many different ways to measure vibration, but the most important thing is to choose a method that will give you accurate results.